
Brain Health
Better Clarity
Not enough folate or too much folic acid can both lead to impaired memory and brain health.
The Folate-B12 Balance: A Delicate Act
The Importance of Folate
Folate, a crucial B-vitamin, plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including:
Brain health: Supporting cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
The Risks of Imbalance
While folate is essential, it's important to maintain a delicate balance:
1. Folate Deficiency:
Cognitive Impairment: Can lead to difficulties in thinking, memory, and learning.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Increases the risk of conditions like Alzheimer's disease.
2. Excessive Folate Intake, Especially in B12-Deficient Individuals:
Hematologic Risks: May contribute to abnormal blood cell formation.
Neuropsychiatric Risks: Can worsen cognitive function and potentially increase the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Understanding the Connection
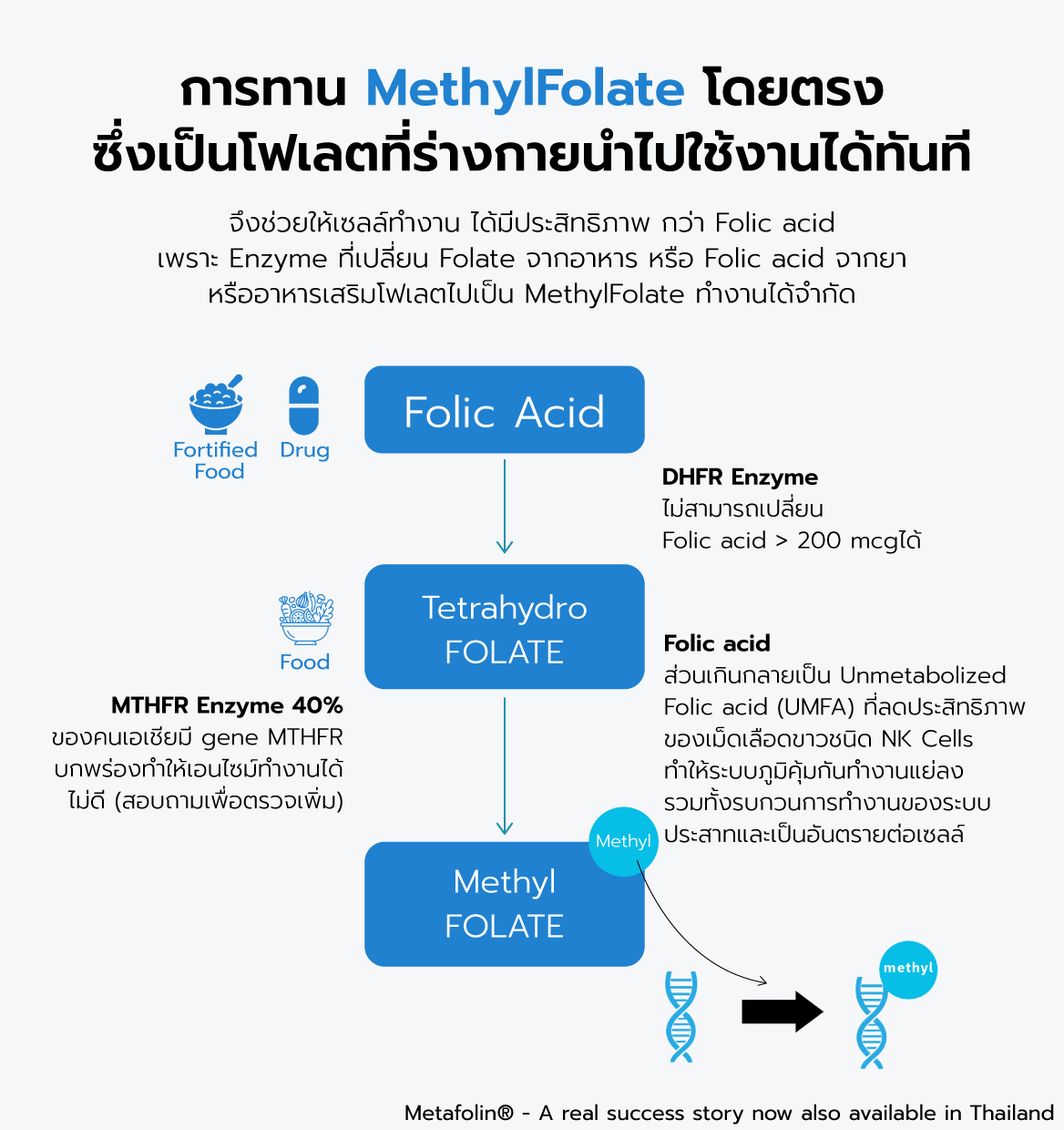
Folate Metabolism: To be utilized by the body, folic acid (the synthetic form of folate) must be converted to its active form, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF).
Vitamin B12's Role: Vitamin B12 is essential for this conversion process.
High Folate, Low B12: When folate intake is high, but B12 levels are low, the body may struggle to convert folic acid into its active form. This can lead to a buildup of unmetabolized folic acid (UMFA), which has been linked to various health issues.
Citation:
1. Savaria, The American Journal of Clinical Nutriton, 2010
2. Moore, J Alzheimers Dis. 2014
The Bottom Line
While folate is essential for optimal health, it's crucial to maintain a balanced intake and ensure adequate vitamin B12 levels.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you have concerns about your folate or vitamin B12 levels, or if you're considering supplementation, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.


















Unlock Your Health's Potential with Methylfolate
Experience the Power of Bioactive Folate
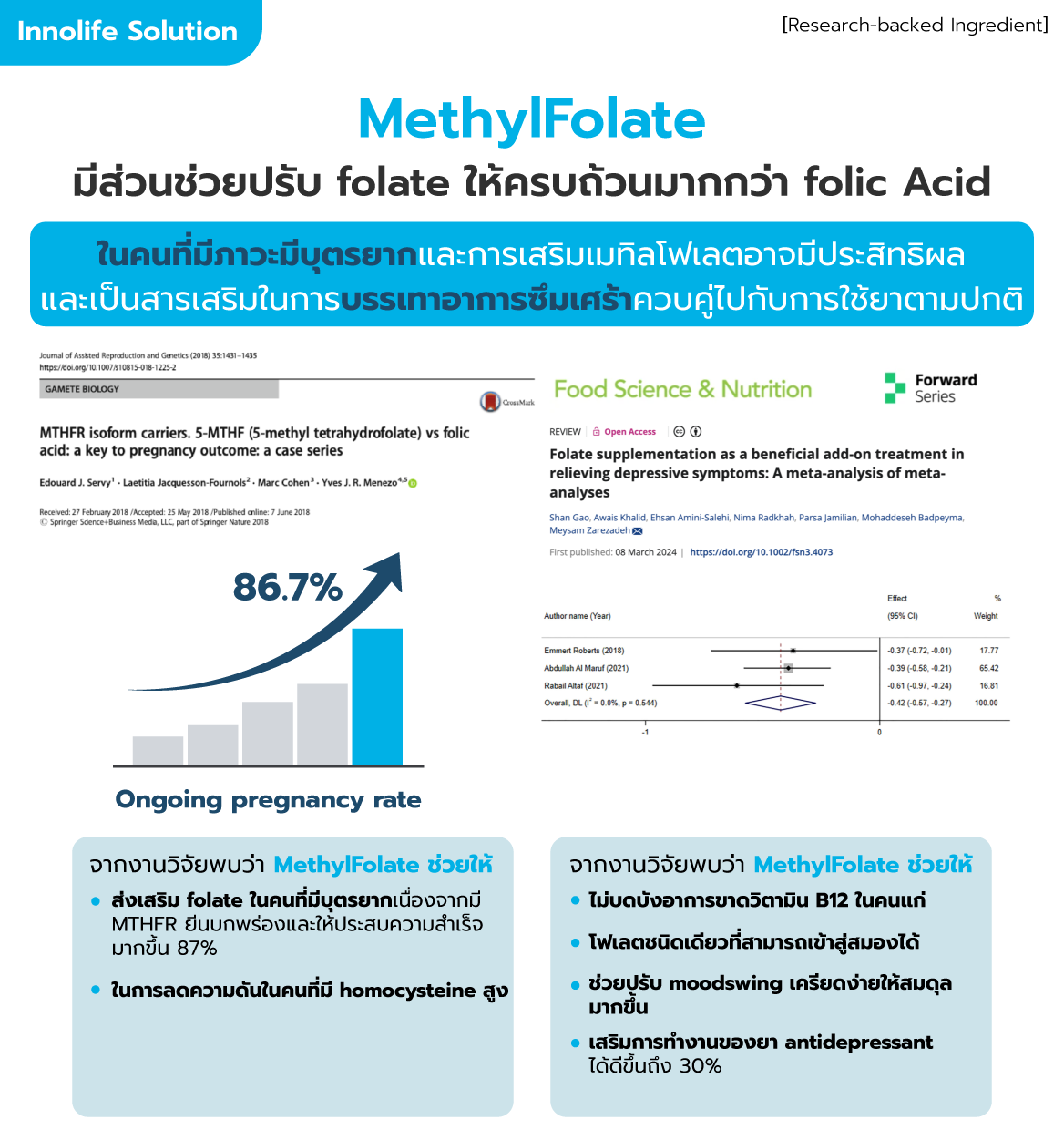
Clinical studies prove Methylfolate (Metafolin®) enhances vital organ function, promoting healthy aging from the inside out. Unlike regular folic acid, Methylfolate is a bioactive form of folate your body can use immediately, maximizing its benefits.
Key Benefits:
- Anti-Aging: Supports efficient cell function through optimal DNA methylation and gene expression.
- Brain Health: May help prevent dementia and Alzheimer's, and reduce stroke risk.
- Heart Health: Contributes to reducing heart disease and diabetes risk.
- Maternal & Infant Health: Crucial for preventing neural tube defects (NTDs) and reducing diabetes risk during pregnancy.
- Mood & Stress: Helps maintain balanced neurotransmitters (Dopamine and Adrenaline) for a more positive mood and reduced anxiety and stress.
The Methylfolate Advantage:
Methylfolate acts as a vital messenger, delivering methyl molecules to your DNA. This precise control over gene activation and deactivation ensures optimal cell function.
Because your body doesn't need to convert Methylfolate, it's significantly more effective than regular folic acid, especially considering that many people (especially 40% of Asians) have MTHFR gene variations that limit their ability to process folic acid efficiently.
Excess folic acid that your body can't process can lead to Unmetabolized Folic Acid (UMFA), which can negatively impact immune function and nervous system health.

Specifically for Expectant and Nursing Mothers:
Prioritize your health and your baby's development with our specially formulated Methylfolate supplement. This essential nutrient is crucial throughout preconception, pregnancy, and breastfeeding, periods when nutritional needs dramatically increase. Our formula is designed to meet these unique needs, supporting both mother and baby every step of the way.
Benefits at Each Stage:
- Preconception: Provides vital nutrients from the moment of conception.
- First Trimester: Supports healthy brain and spinal cord development with bioactive 5-MTHF.
- Third Trimester: Provides essential nutrients for continued fetal development and prepares mother and baby for childbirth.
- Postpartum & Breastfeeding: Supports increased dietary needs and reduces the risk of postpartum blues.
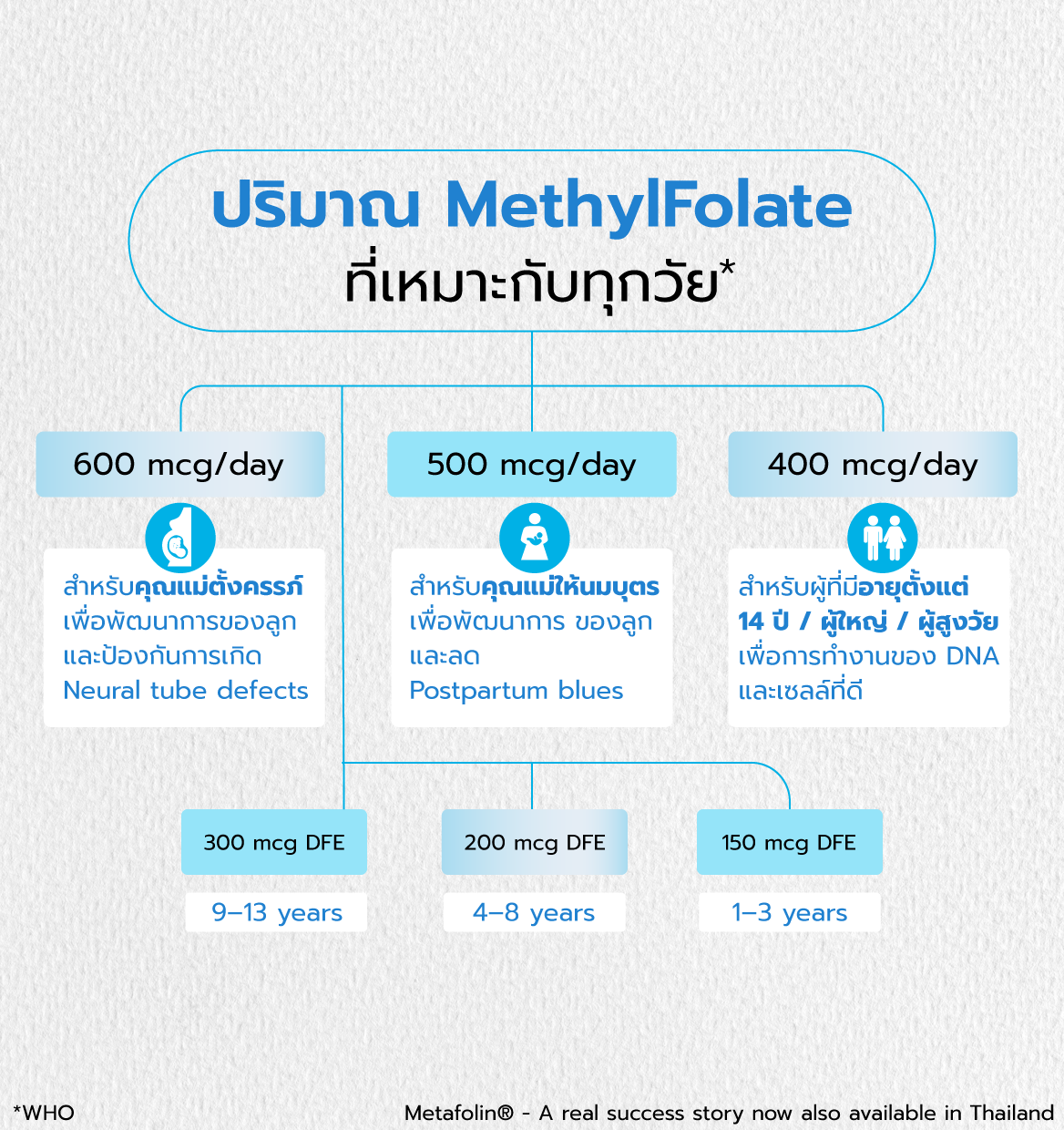
Recommended Daily Dosage (WHO Guidelines):
- Breastfeeding Mothers: 600 mcg/day (Supports baby's development and reduces postpartum blues)
- Pregnant Women: 500 mcg/day (Supports baby's development and prevents NTDs)
- Adults (14+): 400 mcg/day (For optimal DNA and cell function)
- Children (9-13): 300 mcg DFE
- Children (4-8): 200 mcg DFE
- Children (1-3): 150 mcg DFE
Directions for Use: Take 1 tablet daily (200 mcg) or as directed by your healthcare professional.
Order yours today and experience the difference!
